
Welcome to my 9CSI Internet Website. This will be used for my Assesment on the Internet in Term 2
Please click here to see our class website on the internet
A browser is a search engines that lets us search through the internet. Different types of browsers are FireFox, Chrome, Safari and Internet Explorer (pictures above). The browser lets the user veiw the site they have searched up. Browsers take us to different webpages like mightyape or trade me. If you are reading this you have used a browser to get to this website. The first Web browser, called WorldWideWeb, was created in 1990. That browser's name was changed to Nexus to avoid confusion with the developing information space known as the World Wide Web.

ISP (Internet Service Provider) provides you your internet and broadband. At home my families ISP is vodafone partly because my dad works at vodafone. Every mounth your Internet Service Provider will charge you a bill. Most internet service providers will give you data, messages and calls for your mobile phone. Your ISP alows us to call and text each other everyday if you pay for it.
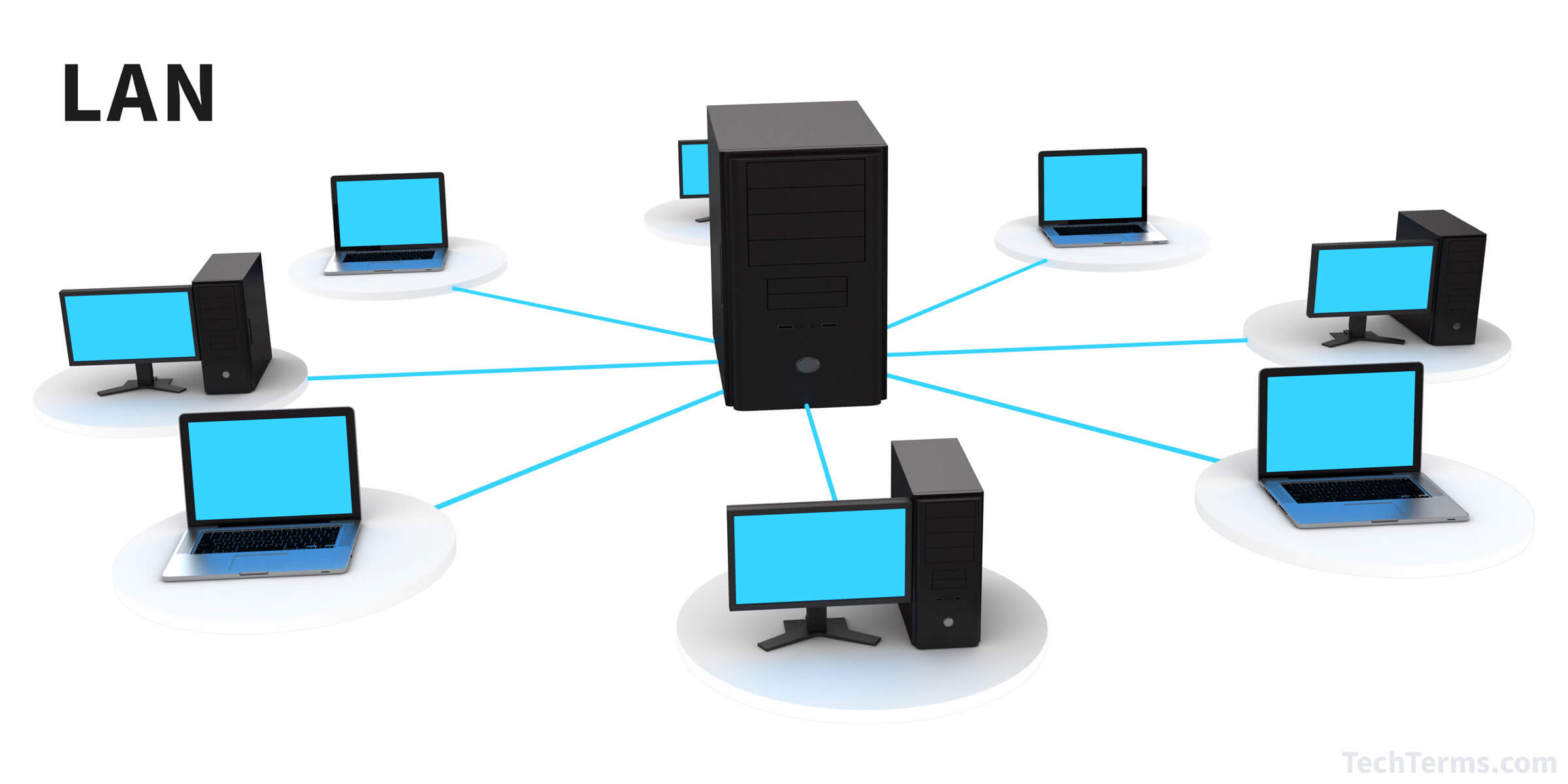
A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and other devices in a small area, typically a single building or a group of buildings. Most LANs connect workstations and computers and let users access data and devices (e.g., printers and modems) anywhere on the network. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two most common technologies in use for local area networks. Computers and other mobile devices use a LAN connection to share resources such as a printer or network storage.

A device is gaget that is made for a particular purpose. An example of a device is a cell phone, and a cell phones has alot of purposes like contacting people and telling people the time. Devices let us download stuff onto them such as games or music. As the years go on more devices are used on a day to day basis. Devices now are ascentual to our learning like computers are a must have in a lot of school around the world, and more and more familys are giving kids cell phones so that they can contact them if they need to.

A user is a person who opperates a device to access a network or the Internet for a purpose. When computers were first invented you needed to be a genius to use a computer. Now children of preschool age are able to use computers or other devices. This has come about by the software devalopment of graphical user interfaces (GUI). These interfaces guide users through various functions.
Web pages are what make up the World Wide Web. A web page is a hypertext document connected to the World Wide Web. To view a web page requires a browser (e.g. Internet Explorer, Edge, Safari, Firefox, or Chrome). Every Web page has its own IP adress and domane name. Web pages can either be static or dynamic. Static pages show the same content each time they are viewed. Dynamic pages have content that can change each time they are accessed.
The world wide web was invented by Tim Berners Lee. The World wide web is an information system on the Internet which allows documents to be connected to other documents by hypertext links, enabling the user to search for information by moving from one document to another. But the world wide web can be a dangerous place, a lot of people are getting random emails saying you just won one million dollars, please enter your email adress, password and credit card details to receive what you have won. And it turns out it was just scam to get your details and get your money.

A modem is a device that provides access to the Internet. Cable modems have a coaxial (or "coax") connection, which is the same type of connector found on
a TV or cable box. While early routers provided several Ethernet ports for wired connections, most modern routers offer wireless connectivity as well. Wireless routers allow multiple computers and other devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to join the same network.
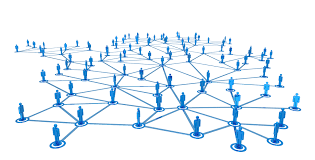
A network is a bunch of computers connected by a server. It can be as small as two computers or as large as billions of devices. Many types of networks exist, but they fall under two primary categories: LANs and WANs. An example of a network is the Internet, which connects millions of people all over the world. One of the first computer networks to use packet switching, ARPANET was developed in the mid-1960s and is considered to be the direct predecessor of the modern Internet. The first ARPANET message was sent on October 29, 1969.

There are big computers that are called webservers. All computers that host Web sites must have Web server programs. A webserver stores, processes and delivers web pages to people. Every Web server has an IP address and a domain name. For example, if you enter the URL http://www.webopedia.com/index.html in your browser, this sends a request to the Web server whose domain name is webopedia.com. Web servers often come as part of a larger package of Internet- and intranet-related programs for serving email, downloading requests for File Transfer Protocol (FTP) files, and building and publishing Web pages.
Fiber optic cables are used to connect our world today. They are capable of transmitting information across countries and oceans. You can see what fiber optic cables look like in the video above. Digital data is transmitted through the cable via rapid pulses of light. The receiving end of a fiber optic transmission translates the light pulses into binary values, which can be read by a computer. Because fiber optic cables transmit data via light waves, they can transfer information at the speed of light. Not surprisingly, fiber optic cables provide the fastest data transfer rates of any data transmission medium. For example, some ISPs now offer "fiber Internet," which provides Internet access via a fiber optic line. Fiber connections can provide homes and businesses with data transfer speeds of 1 Gbps.
.png)
Web hosting is an activity or business of providing storage space and access for websites. In order to publish a website online, you need a Web host. The Web host stores all the pages of your website and makes them available to computers connected to the Internet. A Web host can have anywhere from one to several thousand computers that run Web hosting software. If you want to publish your own website, you'll need to sign up for a "Web hosting service." Finding a good Web host shouldn't be too hard, since their are thousands available. Just make sure the Web host you choose offers good technical support and ensures little or no downtime. You'll usually have to pay a monthly fee that varies depending on how much disk space and bandwidth your site will use.
A packet is the unit of data that is routed between an origin and a destination on the Internet or any other packet-switched network. Any time you receive data from the Internet, it comes to your computer in the form of many little packets. Each packet contains the address of its origin and destination, and information that connects it to the related packets being sent. Packets from many different locations can be sent on the same lines and be sorted and directed to different routes by various computers along the way. It works a lot like the post office, except billions of packets are transferred each day, and most packets take less than a few seconds to reach their destination.
 "
"
Some of the first routers provided several Ethernet ports for wired connections, most modern routers give us wireless connections as well. This is a hardware device that routes data (hence the name) from a local area network (LAN) to another network connection. A router acts like a coin sorting machine, allowing only authorized machines to connect to other computer systems. Most routers also keep log files about the local network activity. In order for devices on the network to connect to the Internet, the router must be connected to a modem.
 "
"
Regional area network (RAN) is a networking technology that uses underutilized parts of the radio frequency (RF) spectrum to provide Internet connectivity for homes and businesses, particularly in underserved areas. WiFi covers only about a few blocks but RANs uses wireless singal 400 to 700Mhz range, which enables greater range and penetration of obstacles.
 "
"
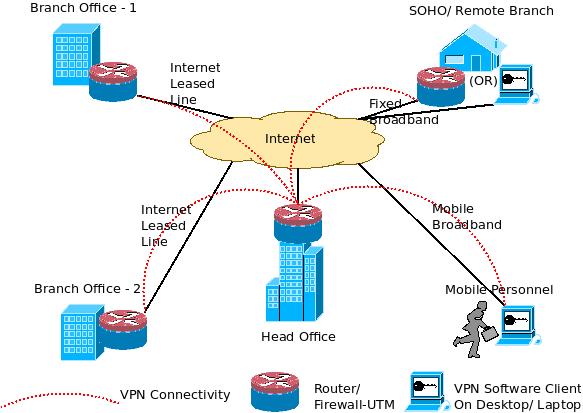
A wide area network (WAN) is a geographically distributed private telecommunications network. It connects multiple local area networks (LAN's) that are geographically seperated. In some instances the distance can be hundreds or kilometers aprt. In a modern WAN routers and switches are connected by fixed line (Fibre optical cable) or wireless technology. The above picture shows a banks WAN that connects multiple locations and services together.